Atomic Radii
Atomic and Ionic Radius
Definition
An atomic radius is generally defined as the total distance from the nucleus of an atom to the outer orbital of an electron. In simple terms, it can be defined as something like a radius of a circle, where the center of the circle is the nucleus and the outer edge of the circle is the outer orbital of the electron. As you begin to skip or drop the periodic table, trends appear that help explain how atomic radii change.
Active nuclear charge atomic positive charge electron valence. Another good charge is the protection of the main electrons and therefore the positive charge does not affect the electron valence. A detailed description of the defense and cost of active nuclear can be found here. Active nuclear charge greatly affects the atomic size of the atom. So as Active nuclear charge decreases, the atomic radius will increase because there are more testing of electrons from the nucleus, which reduces the attraction between the nucleus and the electron. As Active nuclear charge descending in a group and right to the left across the atomic table, the atomic radius will move up and down the group and right to the left across the periodic table.
Types of Rates With respect to Bond Types
Determining an atomic atom is very difficult because there is uncertainty in the outer electron area. We do not know exactly where the electron is. To obtain an accurate radius, but still not a perfectly accurate measure, we determine the radius based on the distance between the nuclei of two bound atoms. Atomic radii are therefore, determined by constructive bonds. An atom will have different radius depending on the constructive bond; therefore, there is no fixed atomic radius.
Covalent Radius
If a covalent bond exists between two atoms, the covalent radius can be determined. When two atoms of the same element are joined together, the radius of each atom will be a fraction of the distance between the two nuclei because they attract the electrons equally. The distance between the two nuclei will give the atomic diameter, but you need a radius half the width.
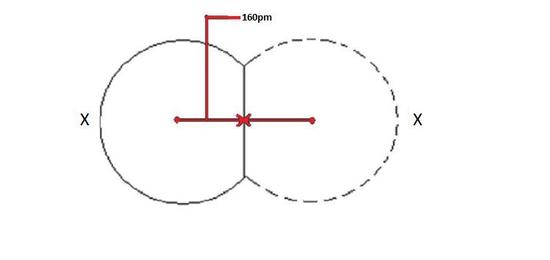
Covalent radii will grow in the same pattern as atomic radii. The reason for this practice is that when the radii are large, the distance between the two nuclei increases.
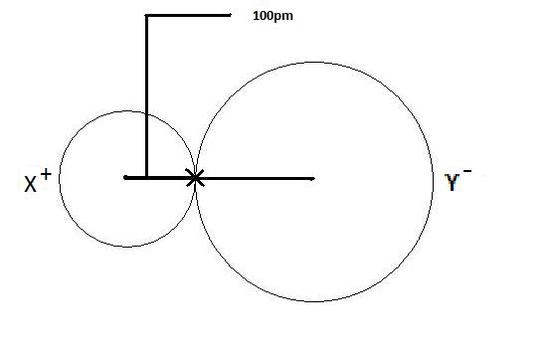
An anion, on the other hand, will be much larger than the atom made of it because of the electron advantage. The electron gain adds more electrons to the outer shell which increases the radius because there are now more electrons away from the nucleus and more electrons will pull into the nucleus so that gravity is slightly weaker than a neutral atom and causes an increase in atom.
Metallic Radius
Metal radius is an atomic radius composed of a metal bond. Metal radius is part of the total distance between the nuclei of two adjacent atoms in a metal cluster. Since a metal is a group of atoms of the same substance, the distance of each atom will be the same.
Trends of Atomic Radius Times
The atom becomes larger as the number of electronic shells grows; thus the atomic radius increases as it descends by a certain group in the periodic table of objects.
Generally, the size of an atom will decrease as it moves from left to right for a period of time.
The radius of atoms increases as you descend from a certain group.
Horizontal Trend
The size of the atom will decrease as it goes from left to right.

PROVINCIAL: Because the electrons added to the changing material are added to the inner electron shell and at the same time, the outer shell remains unchanged, the nucleus pulls the electrons inwards. The electron configuration of the conversion metals explains this situation. That is why Ga is about the same size as its previous atom, and why Sb is slightly larger than Sn.


You must be logged in to post a comment.