World War I
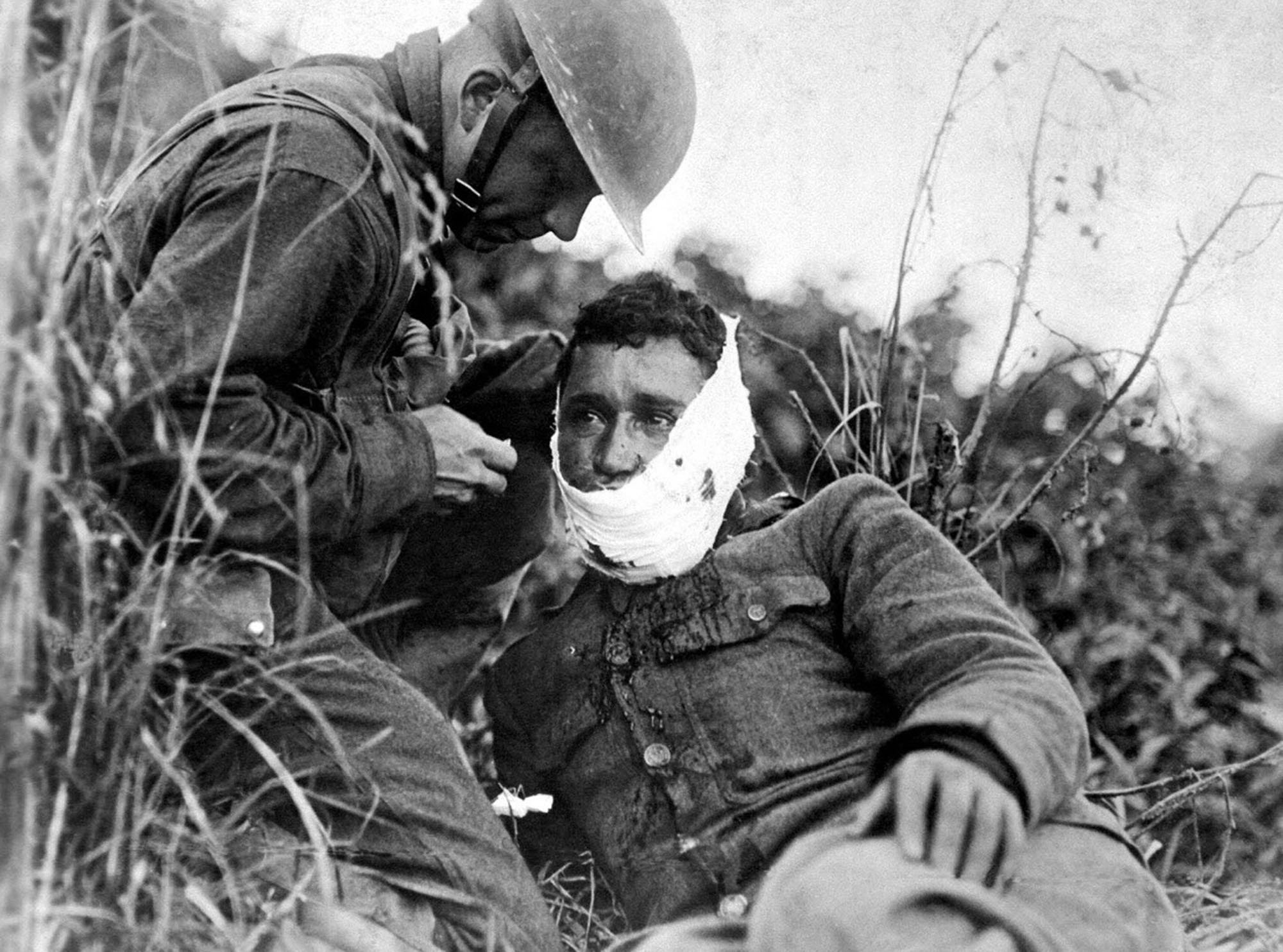

World War I was a global war that lasted from 1914 to 1918. It involved the majority of the world's nations—including all the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Central Powers. It was the most widespread war in history and directly involved more than 100 million people from more than 30 countries. In a state of "total war", the major participants threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, erasing the distinction between civilian and military resources. Marked by mass deaths of civilians, including the Holocaust (in which approximately 11 million people were killed) and the strategic bombing of industrial and population centers (in which approximately one million people were killed), it resulted in an estimated 50 million to over 70 million fatalities.
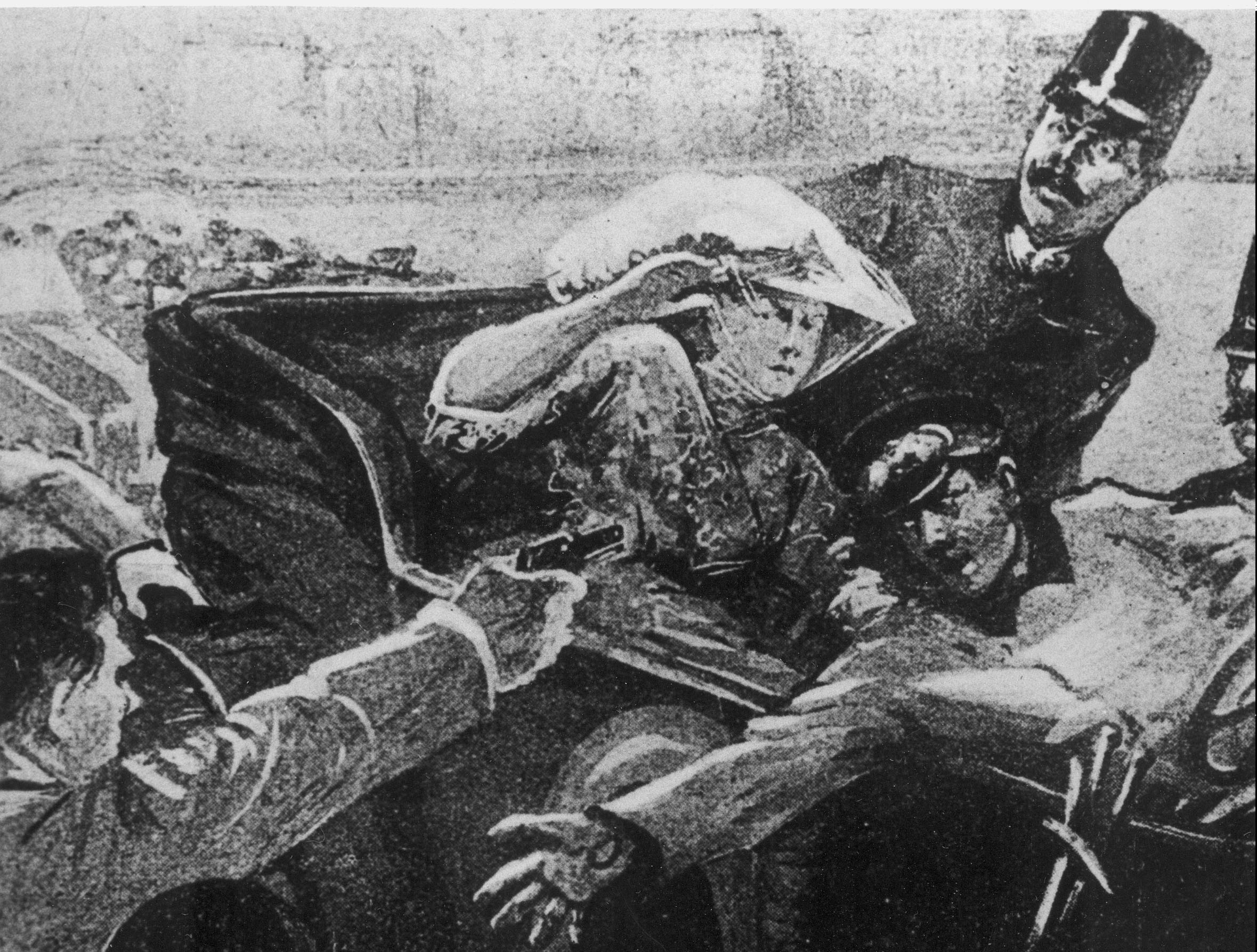
The causes of World War I are still the subject of debate, but it was primarily sparked by the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary on June 28, 1914. This event led to a series of diplomatic crises, and soon various countries began to mobilize their military forces. On July 28, 1914, Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia, and the conflict quickly spread as Germany, Russia, and Belgium also declared war on each other.
The war saw the emergence of powerful new weapons, including tanks, chemical warfare, and the use of aircraft for military purposes. It also marked the end of the traditional European balance of power and the beginning of the modern international system, with the League of Nations serving as a precursor to the United Nations.
The war had a significant impact on global politics and economics, and it is still remembered today as one of the deadliest conflicts in human history.
Here are some additional details about World War 1:
Causes of the war:
- The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary in 1914 was the immediate cause of the war, but it was the result of a complex web of alliances, militarism, and nationalism that had developed among the European powers in the decades leading up to the conflict.
Major players:
- The Allied Powers: The United Kingdom, France, and the Russian Empire (which withdrew from the war in 1917 following the Russian Revolution). The United States also joined the Allies in 1917.
- The Central Powers: Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire.
Key events:
- 1914: The assassination of Archduke Ferdinand leads to the outbreak of war. Germany invades Belgium and declares war on Russia.
- 1915: The war becomes a global conflict with the entry of Italy, Japan, and the United States. The use of poison gas becomes widespread.
- 1916: The Battle of the Somme, one of the bloodiest battles in history, takes place on the Western Front.
- 1917: The United States enters the war on the side of the Allies. The Russian Revolution leads to the withdrawal of Russia from the war.
- 1918: The tide of the war begins to turn against the Central Powers. Germany's spring offensive, its last major offensive of the war, is unsuccessful.
- 1919: The Treaty of Versailles is signed, officially ending the war.
Impact:
- Over 9 million soldiers and 7 million civilians lost their lives during the war.

- The Russian Empire collapsed and was replaced by the Soviet Union under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin.
- The Treaty of Versailles imposed harsh penalties on Germany, including large reparations payments and the loss of territory. These terms are believed to have contributed to the rise of Adolf Hitler and the eventual outbreak of World War II.

Technology:

- World War 1 saw the development and use of new weapons and technologies, including poison gas, tanks, machine guns, and aircraft.
- Poison gas, which was first used by the Germans in 1915, was highly effective at causing casualties and terrorizing enemy troops.
- Tanks, which were first used by the British in 1916, were heavily armored vehicles that were designed to break through enemy lines.
- Machine guns, which were mounted on tripods and could be fired continuously, were also highly effective at causing casualties.
- Aircraft, which were used for reconnaissance and for dropping bombs, played a significant role in the war.
Total war:
- World War 1 was the first war in which entire nations mobilized their resources to fight. This meant that men, women, and children all contributed to the war effort, either by fighting on the front lines, working in factories, or growing food.
- Governments also took control of industries and resources to support the war effort, leading to a significant increase in government intervention in the economy.
The Russian Revolution:

- The Russian Revolution, which took place in 1917, was a major event of World War 1. It was sparked by a combination of economic, social, and political factors, including Russia's defeats in the war, food shortages, and widespread discontent with the government.
- The revolution, which was led by the Bolshevik Party under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, resulted in the overthrow of the Russian monarchy and the establishment of the Soviet Union.
- The Russian Revolution had significant consequences for the war and for the world at large. It led to the withdrawal of Russia from the war and the spread of communism to other countries.
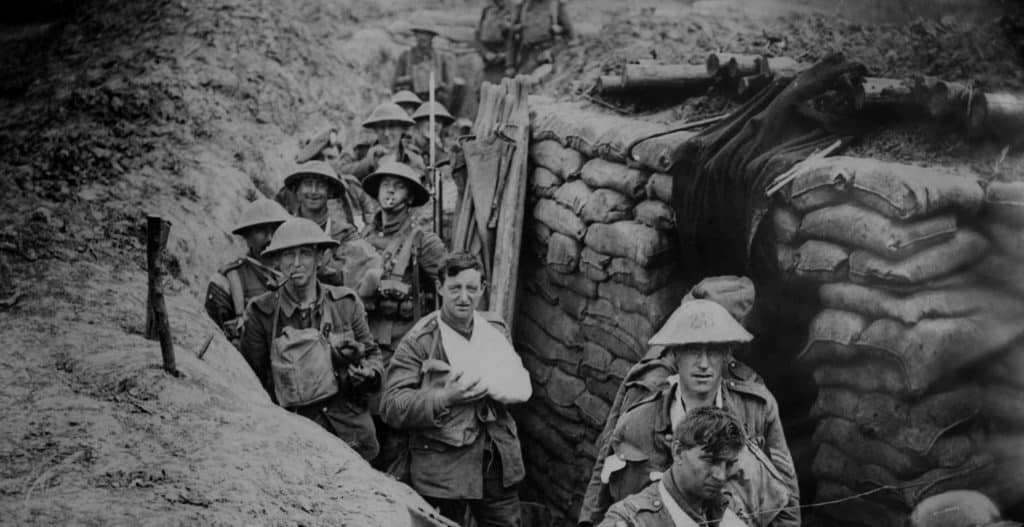
SOME PHOTOS OF WORLD WAR 1 :











You must be logged in to post a comment.