What is the motivation?
Motivation is the process of encouraging people to work to achieve goals. For example, the desire for money, success, recognition, job satisfaction, etc. are the factors stimulating people's behavior. Motivation incentives are used to motivate employees. There are two types of Motivation,
- IncentivesMonetary incentives,
- Non-monetary incentives.
Importance of motivation in business
1. Improves Performance Level in a production.
2. Help to change attitudes of negative or not indifferent.
3. Reduce the Employee Turnover.
4. Helps to reduce absenteeism
5. Lower the resistance to change
Components of Motivation
Motivation theories
The three conventional theories are:
- Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory
- Herzberg’s Two-factor theory
- Theory X and Theory Y
Other theories:
- Equity theory
- McClelland’s Theory of Needs( three needs theory)
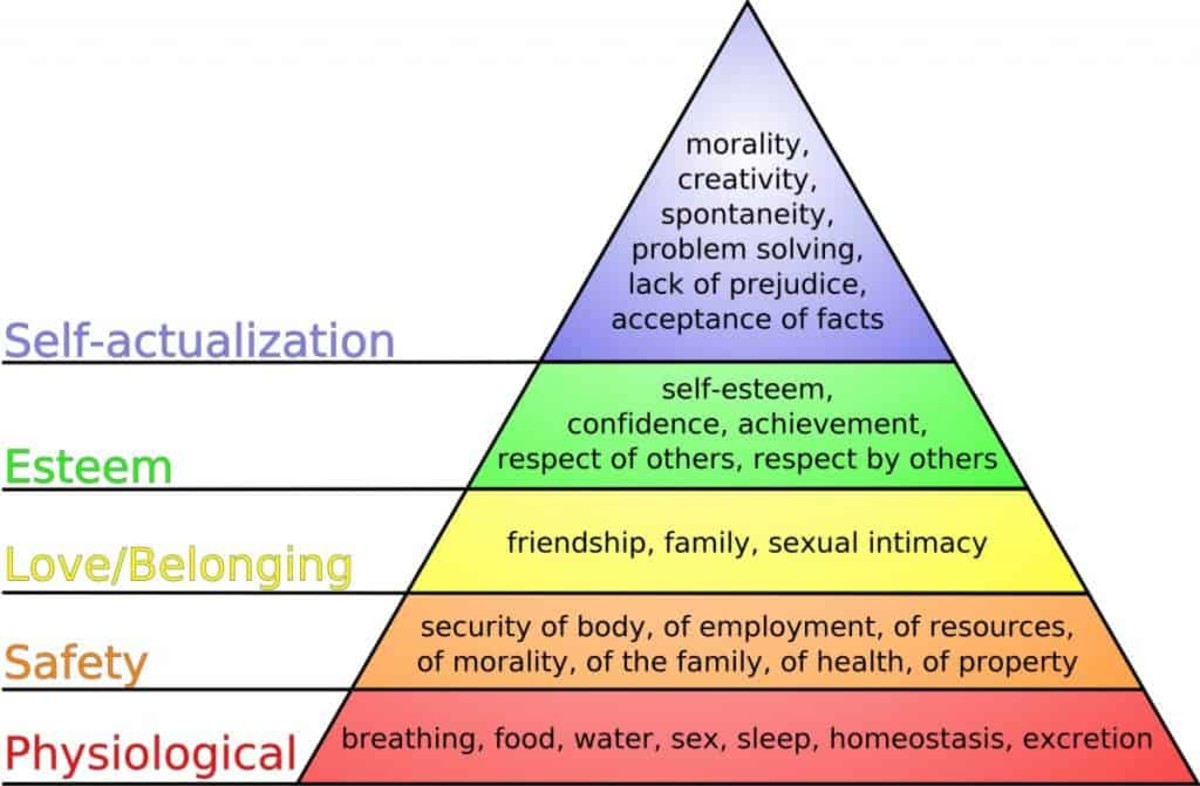
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory
The theory of social, esteem, and self-actualization needs of high-end needs of the states.
- Physiological Needs - The needs of the body, and it's essential for the existence of maintenance.
- Safety Needs – Safety of mental, physical, and status (job).
- Social Needs. - Providing them Social needs, love, affection, security, belongingness, and include the need for companionship.
- Self-fulfillment or Actualization Needs - The knowledge, social service, creativity, and a desire to include taking aesthetic.
- Esteem or Ego Needs - The Internal esteem needs (self-respect, confidence, competence, achievement, and autonomy) and the external esteem needs (recognition, power, status, attention, and admiration).
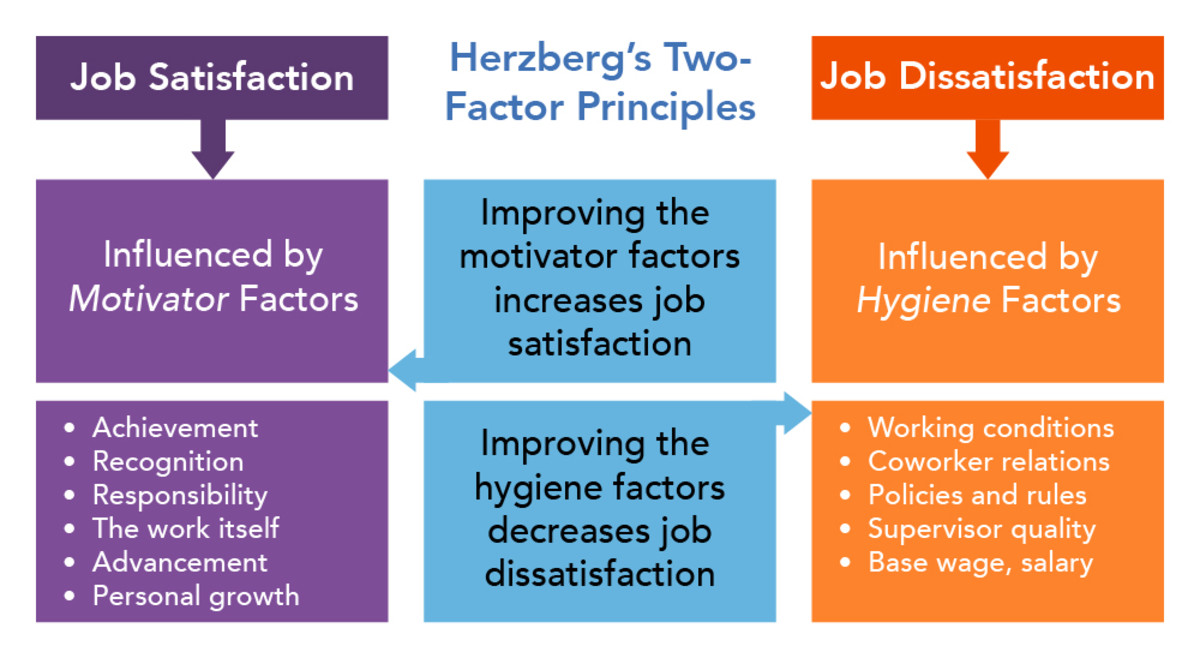
Herzberg’s Motivation-Hygiene Theory
Hygiene factors,
-
Pay - Give competitive wages.
-
Company Policies and administrative policies- Fix obstructive and poor company guidelines, plans, procedures, insurance, policies, and regulations
-
Fringe benefits- give extra facilities than a basic facility.
-
Physical Working conditions
-
Status- Building works conditions by providing meaningful work for all posts.
-
Interpersonal relations- Provide effective, non-intrusive, and supportive supervision.
-
Job Security- makes a good image of the stability of the job.
· Motivators,
- Achievements - provide opportunities for achievements.
- Recognition - recognize their contributions
- Advancement - give them internal promotions.
- Work it self - rewarding them for their achievements (worker of the year).
- Responsibilities - by promotions and make their responsible level high.
Mcgregor’s Theory X and Theory Y
Mcgregor introduced these two theories based on two separate perspectives on human beings, Theory X and Theory Y,
- Theory X,
- It is based on a traditional approach to human behavior,
- Every ordinary person cannot always work the birth; he will try to reduce.
- Let all other factors mentioned relate to most workers. These assumptions are negative vis-à-vis human nature.
- Theory Y,
- No ordinary man inherently dislikes work. He can view work as natural or enjoyable as the rest or play.
- The attainment of which they committed employees will also exercise self-direction and control.
- In the right conditions, one can learn to accept responsibility for even the average person.
- Commitment to objectives is a function of the rewards associated with their achievement.
- Not all creative people can make decisions and decision-making positions in public management from the same province.
McClelland’s Theory of Needs (three needs theory)
This theory concentrates on three needs: achievement, power, and affiliation. They are :
- Need for Achievement-Excel, to achieve the standards set with regard to the push effort to By giving them challenges.
- Need for power - The need to behave in a way others do not behave. By empowerment.
- Need for the affiliation -The desire for friendly relations and close interaction.- by performing the best in the cooperative.
Equity theory
Employees perceive what they get from a job situation(outcomes) in relation to what they put into it (inputs) and then compare their input-output ratio with the input-output ratio of relevant others
|
Ratio Comparison |
Perception |
|
O/I a < O/I b |
Under-rewarded (Equity Tension) |
|
O/I a = O/I b |
Equity |
|
O/I a > O/I b |
Over-rewarded (Equity Tension) |
So, there won’t be any argument with regrades to that and everyone will look in to earn more.
Conclusion
Motivation is a method to encourage people to work towards the goals. There are many theories to motivate people. Some of the motives involve money, and some aren't.
“You cannot always control what goes on outside. But you can always control what goes on inside.” – Wayne Dyer


You must be logged in to post a comment.